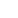Ecological resources become ‘immovable property’ guaranteeing people’s happy life in Tibet
By utilizing its natural resource endowments, Nyingchi city in southwest China’s Tibet autonomous region has helped more and more local people increase their income by engaging in eco-friendly planting, gradually transforming its rich ecological resources into local residents’ proud “immovable property” that guarantees their happy life.
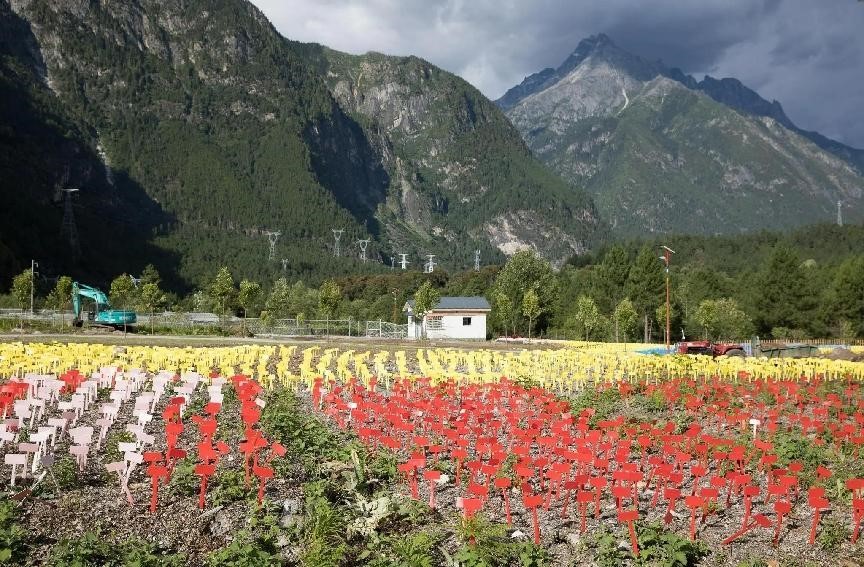

Photo shows a gastrodia elata planting base in Bome county, Nyingchi city, southwest China’s Tibet autonomous region.
Nyingchi city, located in the southeast of Tibet, is at the lowest altitude. It has the warmest and wettest climate, the best ecological environment, and the richest biodiversity among all cities in Tibet. It is also one of the three major primitive areas in China and has long been known as the “Jiangnan of Tibet” (Jiangnan means the fertile and prosperous area in the southern regions of the Yangtze River).
Since the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has a delicate ecological environment, heavy industry and production modes that cause heavy pollution are unsuitable for the region. To conserve the ecological environment while boosting production and improving people’s quality of life, Nyingchi needed to find a right development path first toward modernization featuring harmony between humanity and nature.
The geographical position, favorable climate, healthy ecological environment, and abundant natural resources of Nyingchi have made it a place of great natural endowments for developing understory plants. Based on its advantages, the city has blazed a trail for coordinating ecological protection and appropriate utilization of ecological resources while boosting the eco-friendly growth of industries and realizing the economic value of ecological resources.
Gastrodia elata, a traditional Chinese herb, is one of the understory plants that have changed the life of people in Nyingchi.

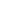
Snow-capped mountains, blue sky, and white clouds turn Bome county, Nyingchi city, southwest China’s Tibet autonomous region, into a fairyland on earth. (People’s Daily Online/Lu Wenkai)
“These five tubers of Tibetan gastrodia elata (a variety of the traditional herb) weigh more than one kilogram and can be sold for over 400 yuan ($61.84) at market price. Compared with gastrodia elata in other regions, the herb in the highlands of Bome county, Nyingchi, has better quality, though with a lower yield, thanks to the sound ecological environment,” Qiu Quanlei, executive with a company that engages in the production and sale of Tibetan gastrodia elata, told People’s Daily in a dense forest on the side of the No. 318 national highway in Nyingchi.
The Tibetan gastrodia elata growing under trees in the forest are marked with signs of different colors in the field.
According to Qiu, who is also dubbed “Doctor Gastrodia Elata”, although the gastrodia elata produced in Bome county is of high quality, the local Tibetan gastrodia elata industry had trouble finding a good breakthrough point for standing out among competitors.
Just when the company didn’t know what to do to change the situation, Zou Yonggang, executive deputy secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Bome county committee came to help.
“We invited the company to invest in here, and we have responsibility to help it get on track and run smoothly,” Zou said.
Thanks to the support of the local government, in April 2021, the working team of Guangzhou, capital of south China’s Guangdong province, which was established under the country’s “pairing assistance” program to help Tibet with its development, reached an agreement with JD Farm, a modern agricultural base project launched by China’s e-commerce giant JD. com. They decided to build a demonstration base of JD Farm and use it as a breakthrough point to introduce a whole-process information-based management system covering various links of the Tibetan gastrodia elata industry of Bome county, from the production to the storage, transportation, and quality tracing of the herb.
Today, sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) are installed in large numbers in the Tibetan gastrodia elata planting base of Qiu’s company, helping the company realize remote monitoring of the temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors using satellites.
Meanwhile, the intelligent management and control system launched for the industry can realize intelligent decision-making based on data analysis, thus providing science-based guidance on the production of the herb.
“Every tuber has a QR code, through which you can get clear information about the product,” Qiu said to viewers during a livestreaming sales promotion of the Tibetan gastrodia elata of Bome county.
According to Zhang Hu, party chief of the CPC committee of Zhamog township, Bome county, sci-tech talents like Qiu have effectively motivated local people to join the industry, increasing the planting area of cultivated wild Tibetan gastrodia elata in Zhamog township to 1,653 mu (110.2 hectares).

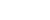
Photo shows beautiful spring scenery of Peach Blossom Valley in Bome county, Nyingchi city, southwest China’s Tibet autonomous region. (People’s Daily Online/Lu Wenkai)
The industrial chain model of the local Tibetan gastrodia elata industrial park, which features benign interactions among enterprises, research institutes, the market and professional growers, is also improving with each passing day, according to Zhang.
The business contributed to a 3.65 million yuan rise in local inhabitants' income, supporting roughly 3,000 farmers and herders, the official added.
While the Tibetan gastrodia elata industry thriving, other characteristic industries of highlands in Nyingchi, such as tea planting, forestry, and fruit and vegetable cultivation, have also experienced rapid development, with tea leaves of Yi’ong township, apple of Mainling county, kiwi fruit of Zayu county, and vegetables of Bayi district of Nyingchi city enjoying great popularity.
So far, the planting area of characteristic forest and fruits has reached 281,000 mu, and that of vegetables and Tibetan herbal medicine 39,000 mu and 16,000 mu, respectively.
Nyingchi is vigorously promoting the construction of tea planting bases in Yi’ong township, Medog county and Zayu county, among other parts of the city, trying to improve the quality and production efficiency of tea products and promote tea brands, according to the mayor of Nyingchi city, who disclosed that the planting area of vegetables in the city will be maintained at more than 40,000 mu.
The Tibetan herbal medicine industry, with Tibetan gastrodia elata as a typical representative, is growing steadily, he said, noting that the city is advancing the construction of a Tibetan herbal medicine industrial park at the level of the autonomous region and building a germplasm bank of Tibetan herbal medicine.
The development path of Nyingchi demonstrates that development and ecology are not mutually exclusive. People’s happy life and continuous improvement in natural environment can be achieved at the same time, and man and nature can coexist in harmony.

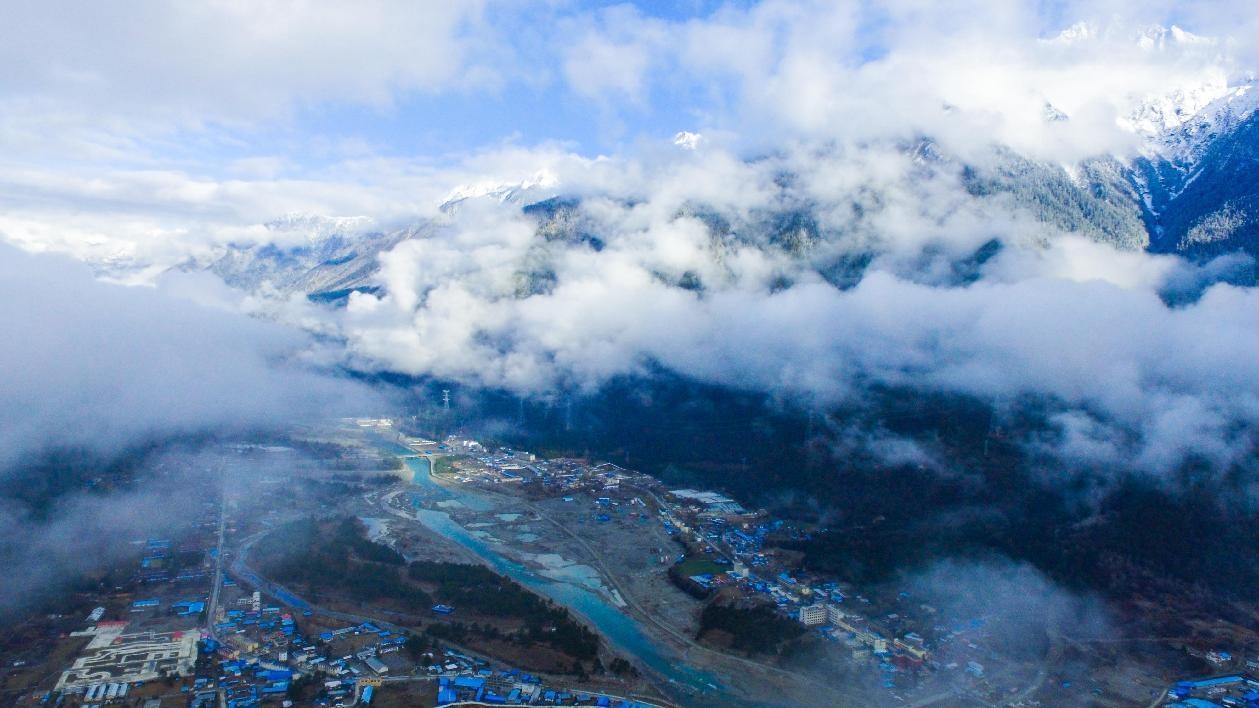
A farmer ploughs his farmland in Bome county, Nyingchi city, southwest China’s Tibet autonomous region, April 3, 2022. (People’s Daily Online/Lu Jianjian)
Photos
 World Book Day: Let's read together
World Book Day: Let's read together Rare silver pheasants flock together in greater numbers to forage at Yishan nature reserve in east China's Jiangxi
Rare silver pheasants flock together in greater numbers to forage at Yishan nature reserve in east China's Jiangxi Young artist takes up brush to create lifelike paintings expressing mankind and nature’s harmonious co-existence
Young artist takes up brush to create lifelike paintings expressing mankind and nature’s harmonious co-existence Cutton farming in full swing in China's Xinjiang
Cutton farming in full swing in China's Xinjiang
Related Stories
- Plateau roads pave way for Tibet's rural revitalization
- Tibet prioritizes ecological protection in development
- Rural roads in Tibet exceed 90,000 km
- Tibet makes progress in prehistoric archaeology research
- Over 1.1 mln folios of ancient texts archived at Tibet's Potala Palace
- Residents pick tea leaves in Medog County, China's Tibet
- Helicopter rises on high to check power line in SW China’s Tibet
- A glance of Lhoba culture in Mainling County, SW China's Tibet
- Beautiful Tibetan village decorated with apricot blossom in Sichuan
- Teenagers in pastoral areas of Tibet attend taekwondo camp
Copyright © 2022 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.