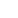2nd phase of conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization launched in SW China

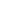
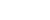
Staff members restore bronze relics at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)

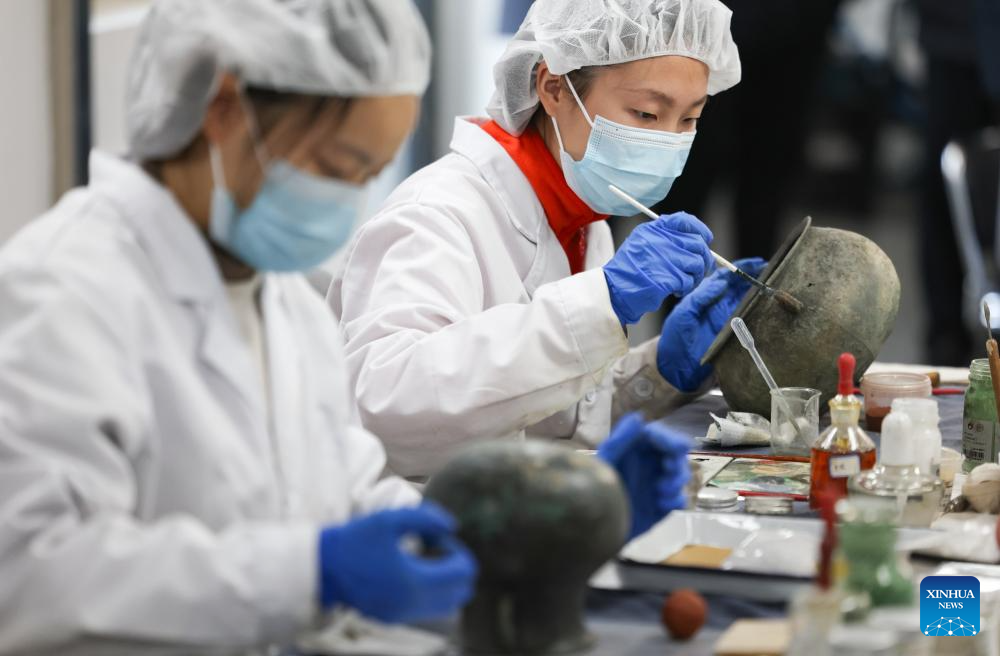
An archaeologist examines a bronze mask at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)

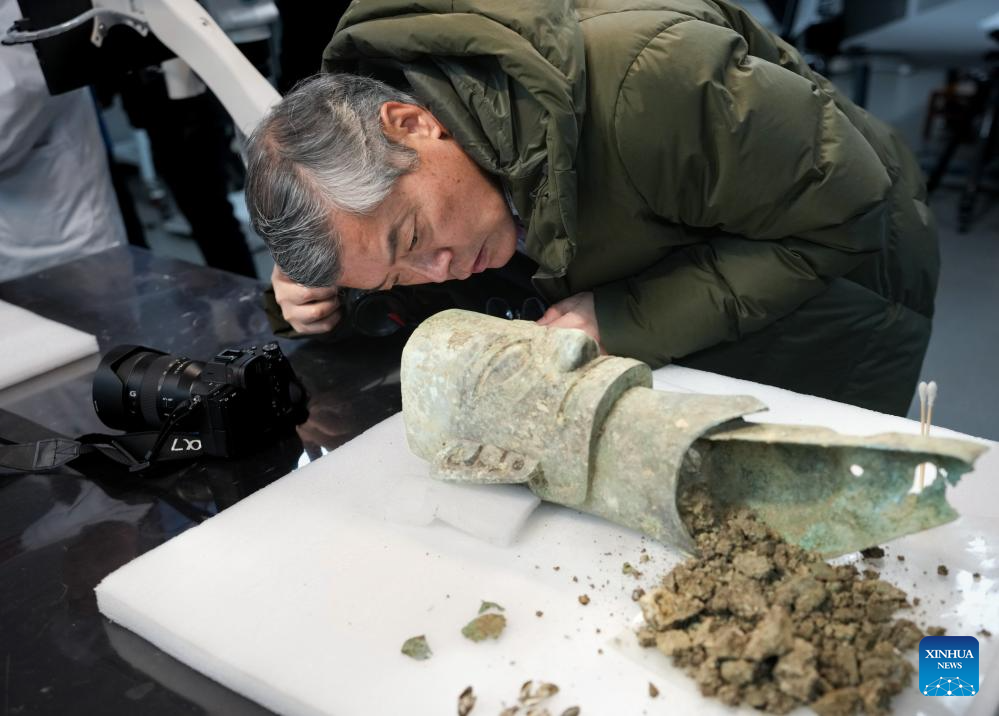
A staff member displays a bronze relic at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
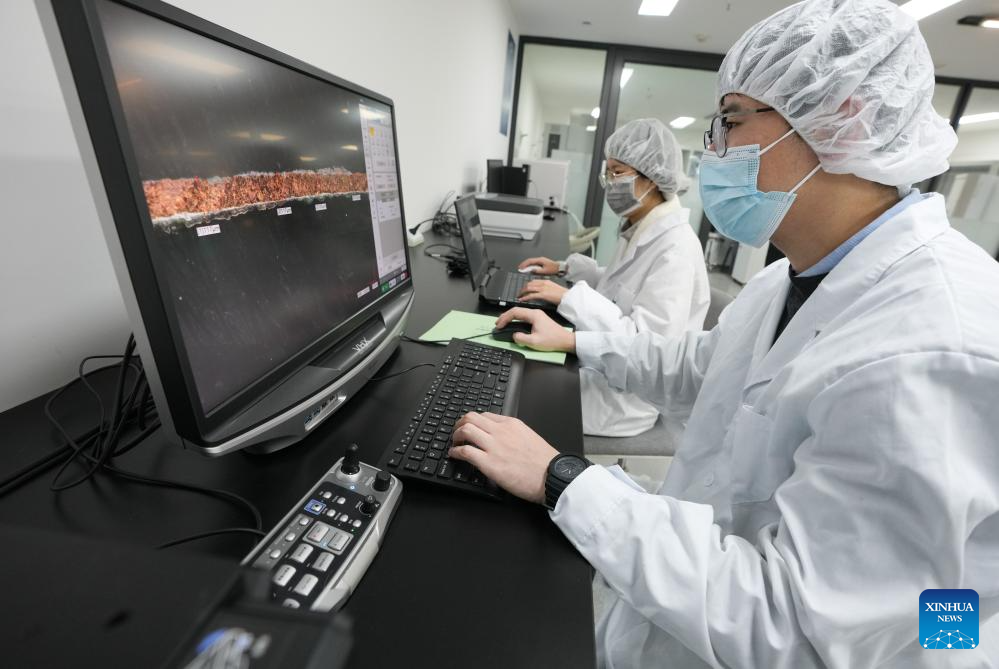

Staff members scan a bronze relic at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
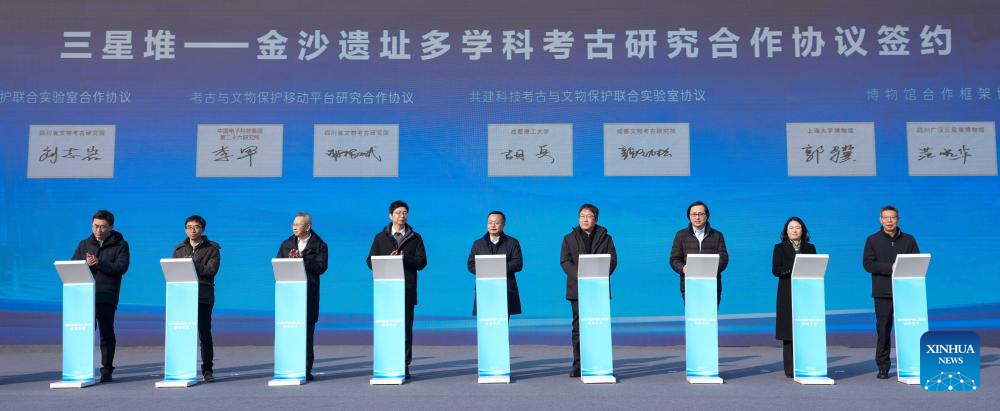

Representatives of archaeological experts sign a cooperation agreement on a multidisciplinary archaeological research on Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
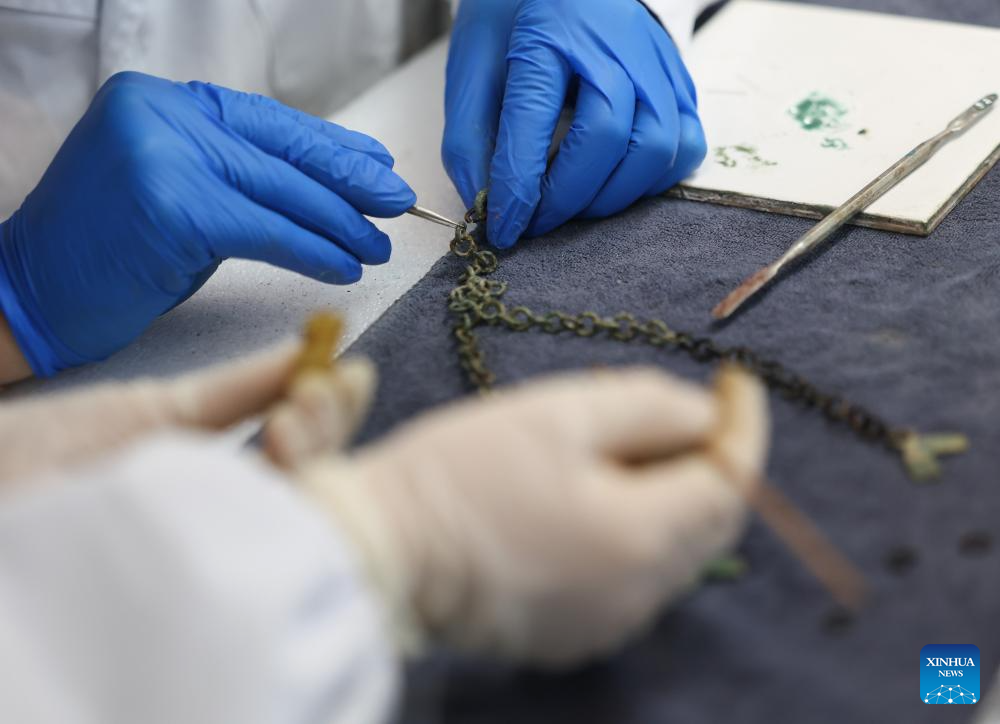

Staff members restore a bronze relic at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
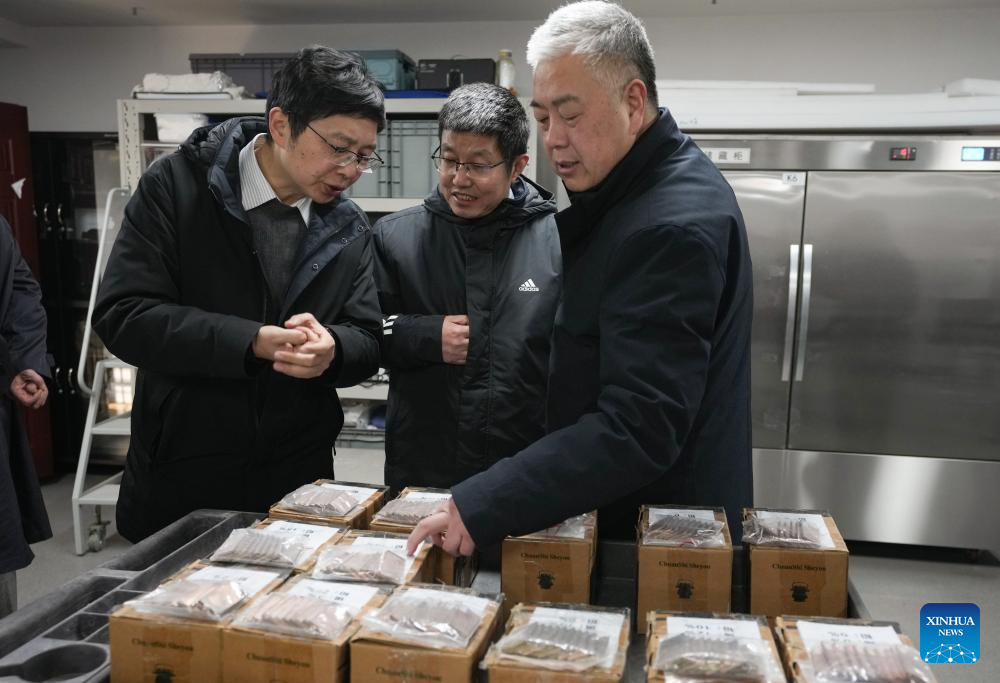

Archaeologists examine samples of bronze pieces with different alloy proportions at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
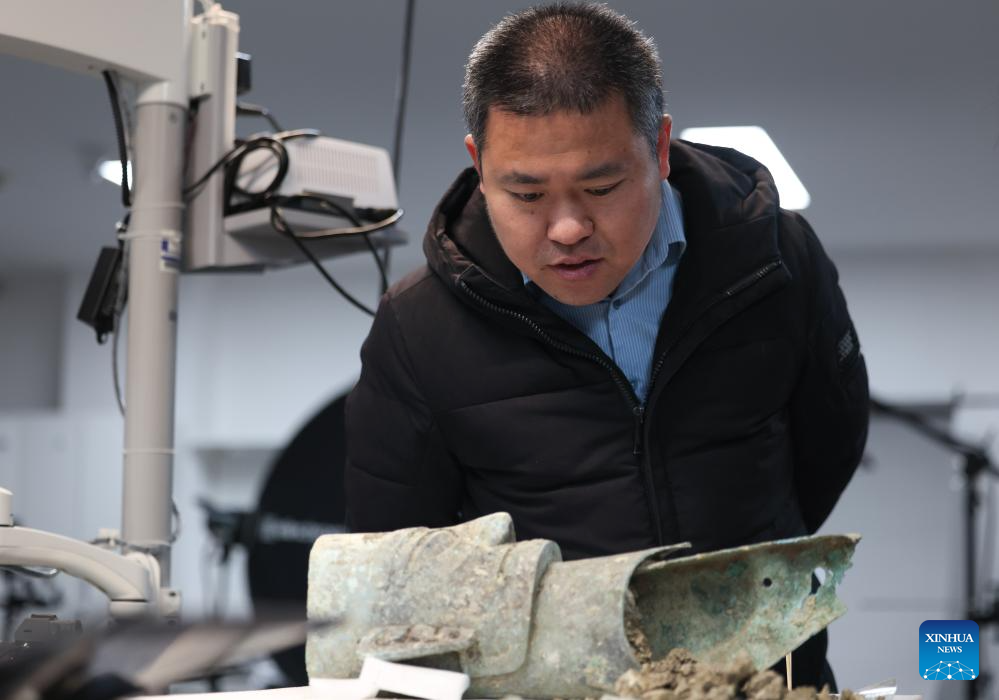

An archaeologist examines a bronze mask at a research institute of Sanxingdui ruins in Guanghan City, southwest China's Sichuan Province, Dec. 16, 2024. The second phase of the conservation and inheritance project of Ancient Shu Civilization was launched here on Monday. In the next three years, excavations and researches will be organized to explore the uncharted territories in the functional areas and important relics of Sanxingdui and Jinsha ruins. Jinsha ruins, together with the Sanxingdui ruins, are peaks of ancient Shu culture and represent the two most glorious periods of the ancient Shu Kingdom that suddenly disappeared about 2,000 years ago. (Xinhua/Jiang Hongjing)
Photos
 International cyclists race through Shenzhen in 2024 XDS Cup
International cyclists race through Shenzhen in 2024 XDS Cup Chinese artisan preserves ancient straw dragon craft, creates 28-meter masterpiece
Chinese artisan preserves ancient straw dragon craft, creates 28-meter masterpiece Migratory birds dance gracefully at lake in N China's Inner Mongolia
Migratory birds dance gracefully at lake in N China's Inner Mongolia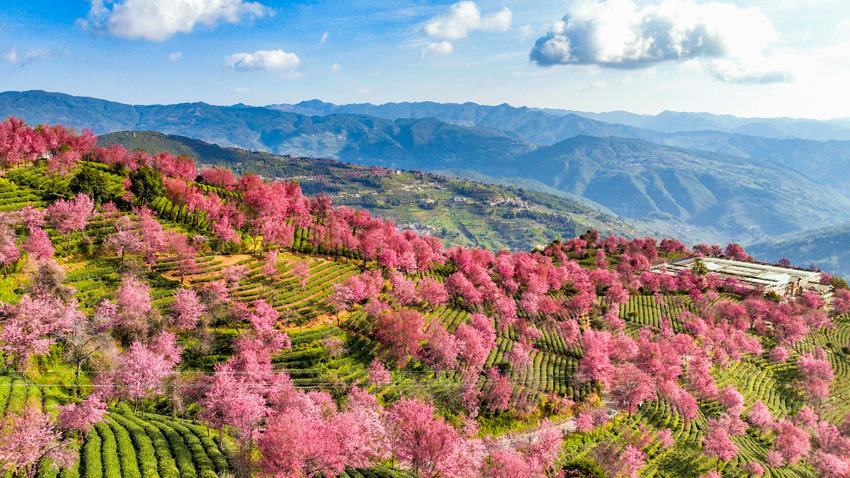 Thousands of cherry blossoms bloom as winter brings spring-like scenery to SW China's Yunnan Province
Thousands of cherry blossoms bloom as winter brings spring-like scenery to SW China's Yunnan Province
Related Stories
- Traces of 10,000-year-old rice beer found in east China
- New study identifies 10,000-year-old alcohol fermentation technique in China
- China discovers landmark human evolution fossils
- Tomb complex dating back to Warring States period discovered in Henan
- 500-year-old Chinese inscription unearthed in western Jerusalem
Copyright © 2024 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.