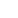Plant growth experiment well underway in lab module Wentian of China's space station
Wentian, the first lab module of China's space station, was launched on July 24. So far, the space lab has been operating well and in-orbit experiments have been carried out as planned.
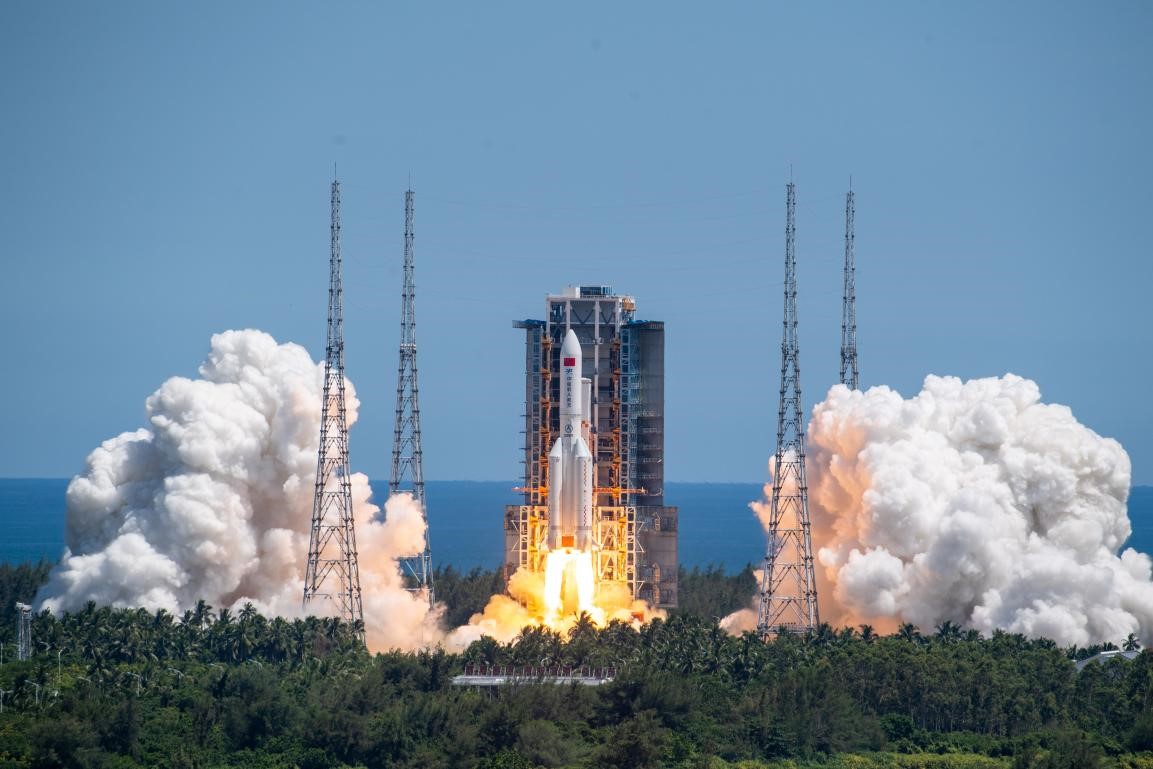

A Long March-5B Y3 carrier rocket, carrying Wentian lab module, blasts off from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in south China's Hainan province, July 24, 2022. (People's Daily Online/Weng Qiyu)
A space growth experiment of thale cress and rice seeds was launched on July 29, and the plants are currently growing well. It marks the first time in the world that full-life-cycle cultivation of rice is conducted in a space station.
The experiment was conducted under the guidance of Zheng Huiqiong, a research fellow at the Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and her team.
It aims to explore how microgravity, the largest challenge for growing plants in space, affects and controls the regulation mechanism of flowering, a key section of plant growth, so as to provide theoretical guidance for improving space planting technologies and space food production.
"The seedlings of thale cress have grown leaves. The rice seedlings have grown to some 30 centimeters high, and short-grain rice to 5-6 centimeters high," said Zheng, adding that the seeds are in good condition.
The experiment is expected to complete a full-life-cycle "from seeds to seeds," and during the process, astronauts will collect samples and then freeze and preserve them, before finally returning them to the ground for analysis.
It is learned that the focus of space growth research has been gradually shifted from seedling growth to seed production. So far, only a few crops have gone through full-life-cycle cultivation "from seeds to seeds," such as oilseed rape, wheat and peas.

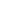
Rice grows in microgravity environment in the Wentian module of China's space station. (Photo from the official website of the Chinese Academy of Sciences)
Zheng hopes the first full-life-cycle cultivation of rice in space can be completed and generate key environmental parameters. Besides, she also hopes to analyze the molecular mechanisms of long-day plants and short-day plants' flowering in microgravity conditions.
Wentian is the second module and the first space lab of China's space station. It houses many experimental cabinets for life science and bioscience.
Zhao Liping, chief designer of the Wentian lab module space application system and researcher with the CAS Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization, said the experimental cabinets are in good condition and experiments have been carried out in an orderly manner.

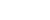
The Wentian module is equipped with a biotechnology experimental system and an ecological life support experimental system developed by Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The two systems are expected to offer continuous support for conducting diverse, large-scale and systematic life science experiments and researches in space. Photo shows a small controlled ecological life support system consisting of zebrafish, aquatic plants and microorganisms. (Photo courtesy of Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences)
The Wentian module offers greater space and more possibilities for researchers to conduct science experiments in space.
The Wentian module, where plants can be cultivated for a longer time, makes it possible to grow rice in space, said Han Bin, CAS academician and director of the Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, adding that the rice growth experiment in space will reveal how rice seeds grow in microgravity and confined environment.
Photos
Related Stories
Copyright © 2022 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.