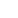Photovoltaic park in NW China’s Qinghai boosts development of clean energy
In addition to producing electricity, a photovoltaic park in the Talatan area of Gonghe county, northwest China’s Qinghai province, is also providing sufficient grass for sheep to survive.
Sitting at an average altitude of 2,920 meters, Talatan is not a suitable place for plants to grow, but with eight hours of daylight a day, it is perfect for photovoltaic power generation.
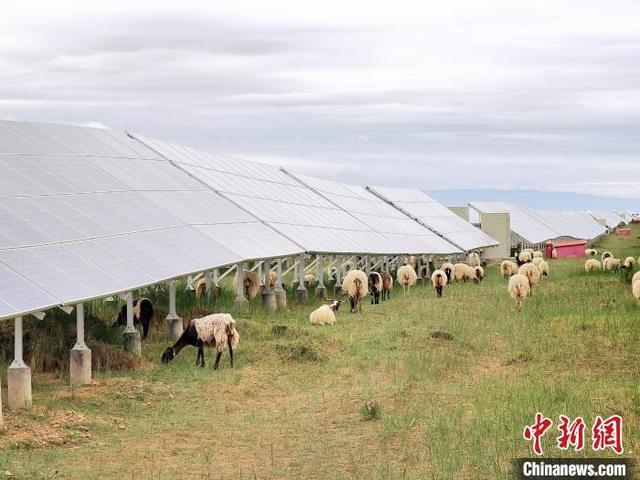

Photo shows sheep grazing on the grassland under solar panels at the photovoltaic park in Talatan area of Gonghe county, Qinghai province. (Photo/Qi Zengbei)
Before the photovoltaic project was established in 2012, Talatan was a desert frequently plagued by sandstorms, and sheep could barely survive there due to the lack of food.
“The solar panels can reduce water evaporation, thus maintaining the soil moisture level for grass to grow and preventing the expansion of desertification,” explained a staff member at the photovoltaic park. With plenty of grass to graze, the sheep grow well, according to a local herder.
However, as the grass grew higher, it started to block the solar panels and affect power generation. To solve this problem, the park invited local farmers to bring their sheep to graze under the photovoltaic panels, according to Tang Jing, deputy director of the information center with the Yellow River Upstream Hydropower Development Co., Ltd, adding that the vegetation coverage rate at the park has now reached 15 percent.
The photovoltaic project has also brought economic benefits to local farmers, as it hires them to clean the solar panels, mow grass, and work as security guards.
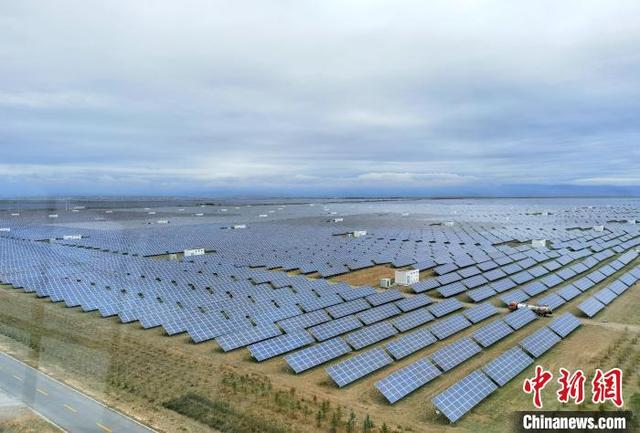

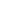
Photo shows the photovoltaic park in Talatan area of Gonghe county, Qinghai province (Photo/Qi Zengbei)
Longyangxia Hydro-photovoltaic Complementary Power Station, with an installed capacity of 850,000 kW, is also located in Talatan. With the help of advanced technologies, Qinghai province converts the unstable electricity generated by the photovoltaic power station into stable, high-quality, and safe electrical energy at the Longyangxia Hydropower Station.
At present, the annual power output of the photovoltaic power station stands at around 1.49 billion kWh, equivalent to 464,600 tons of standard coal and a reduction of 1.22 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
By the end of May 2021, Qinghai saw its output of electricity generated using clean energy sources reach 40.50 million kWh, with the amount of electricity produced by clean energy sources ranking among the first in the country.
Photos
Related Stories
- China makes constant progress of clean energy
- Beijing 2022 set to achieve full supply of clean electricity
- Xi calls on G20 to deepen transition toward clean energy
- China has put in place world's biggest clean energy system: Xi
- "Belt and Road" Clean Energy Development Forum kicks off in Qinghai
- Clean energy helps transform Qinghai’s industrial structure
- China makes great strides in clean energy generation
- Cooperation in clean energy to expand, Xi says
- Clean energy powers northwest China province
- Cleaner energy will be hot topic in winter
Copyright © 2021 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.