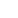John Oxley: Two cities and one journey to World Heritage
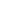
Approaching York from outside, visitors are first greeted by the best-preserved city walls in the United Kingdom, a series of medieval walls that had their foundation from the Roman times. Once a formidable defense against invaders, today, the York City Walls run 3 kilometers long and welcome people from all around the world with unique views of the natural and cultural beauty from the coursing River Ouse to the magnificent York Minster.
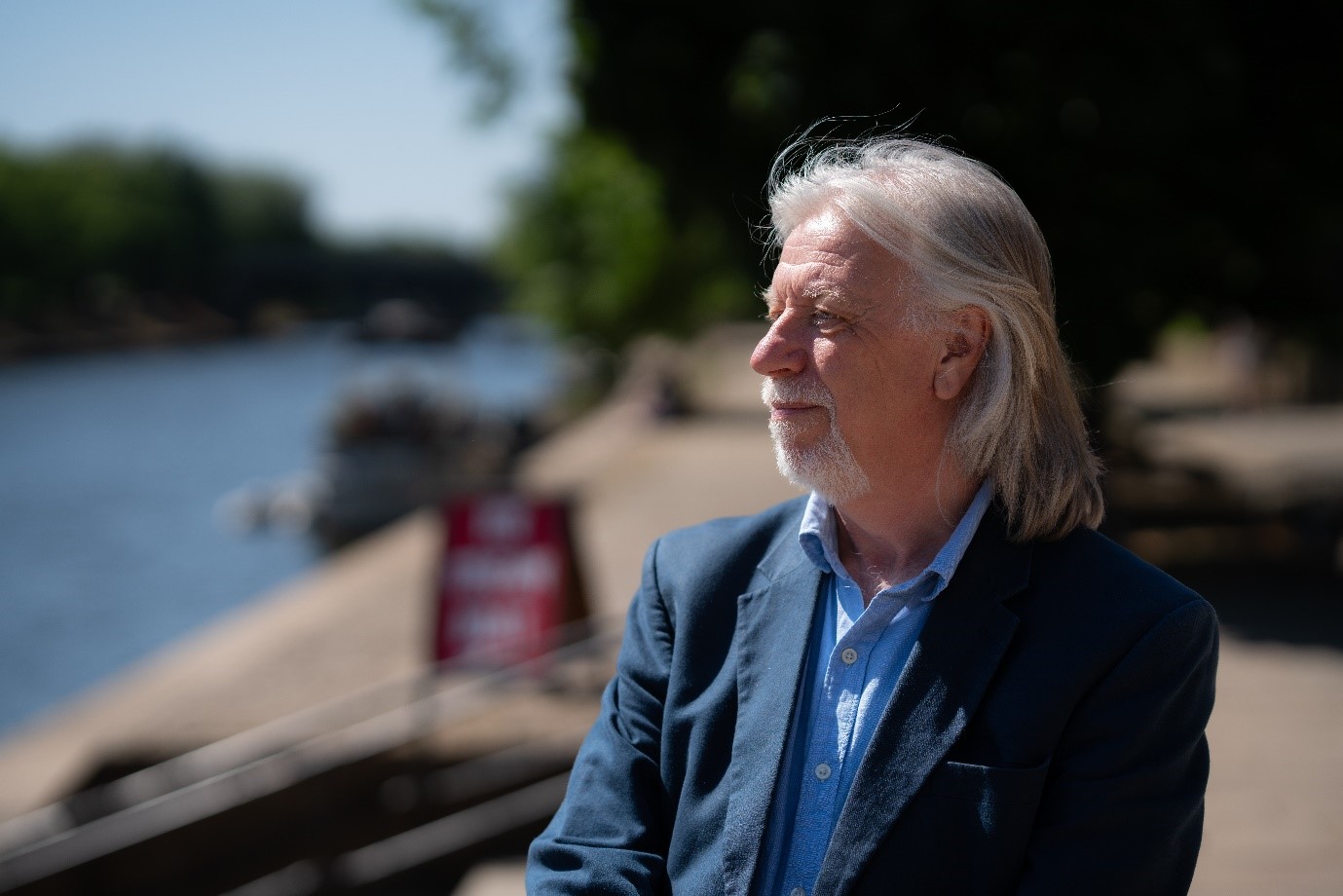
Among those who have guarded this invaluable material heritage for centuries is a Northern man born in a small town outside York, John Oxley. Having had an interest in archaeology since a young age, Oxley held the office of City Archaeologist of York from 1989 to 2019. Under his stewardship and together with his colleagues, the Chinese city of Nanjing became the first Sister City of York in half a century. Now retired and standing on top of the walls that he has looked after for 30 years, Oxley shares with People’s Daily Online the universal values embedded in every stone of the walls around York and Nanjing, and his vision for the two sister cities as future World Heritage sites.
Into the past and into China

John Oxley (Photo/Lewis McCarthy)
People’s Daily Online: For three decades you have worked as City Archaeologist of York. Looking back, your journey into the past started nearly half a century ago and continues today. What was your initial focus and was Chinese history or archaeology taught in the university then?
John Oxley: Indeed, my entry into archaeology came at a very early age when I was eight years old. I wrote an essay at school and the essay was entitled When I Am 20 and I wrote when I am 20, I will be an archaeologist. When I was studying at university and when I was sort of taking part in archaeological projects, there was very little contact with Chinese archaeology and the practice and study of Chinese archaeology.
My interests were heavily European, I'm afraid. So I was focused very much on the archeology of post of Roman and Post-Roman Britain, and that took me through studying for a high end degree at the University of Liverpool.
People’s Daily Online: Throughout your career in archaeology, in addition to excavations of new materials, you have taken on more responsibility in managing existing sites. Can you share with us how this new interest in heritage management enabled your first interaction with China?
John Oxley: So when working in York from 1989 onwards, I developed this framework for managing archaeology and developing this concept of preservation in situ, which allowed us to construct buildings through accepting the destruction of a small amount of archaeology in order to preserve the greater part of the archaeology its significance.
The University of York for a long time had the Institute of Advanced Architectural Studies, and it ran a very prestigious course in conservation and lots of students from around the world came and studied at the Institute. So from about the mid-nineties onwards, we had a reasonably regular visit from people working in the cultural heritage management organizations within the governments of China which was developed through the 2000s.
People’s Daily Online: You mentioned that the link between your work and China can be traced back to the 1990s. What about China generated the most interest? And was there a pivotal moment that made you realize that, in addition to academic exchanges, there was much to achieve in a partnership with your Chinese counterparts?
John Oxley: I think the success that I had in sort of achieving that balance was something that attracted a lot of attention from other countries and quite interestingly, a lot of attention from China, because the problems that they were talking about were very similar to the problems that we had addressed and confronted. It was precisely that problem of the senior politicians and senior officers having an agenda that was driven by developments rather than conservation and so they could see that what we achieved here in York was a program that addressed those political ambitions, but which also actually addressed the need for archaeological conservation and research.
From my perspective, I became aware of the power of that link in 2010 when we hosted a visit by Professor Ruan Yisan from Shanghai and who had established his own Institute for Conservation and did a lot of work on conservation of water towns on the Yangtze River, particularly of the water towns that you've got around Suzhou and Shanghai. That sort of made me realize just how important these conversations and these interactions with academics and conservation practitioners from overseas was.
A tale of two cities

City of York (Photo/Hewitt and Walker)
People’s Daily Online: York formed a twin city relationship with Dijon, France, in 1953 and Munster, Germany, in 1957. In 2016, Nanjing became York’s third sister city and the first outside Europe which led to intensive visits between the two cities. During your first visit to Nanjing, what was your impression of the city and its cultural heritage?
John Oxley: I think it was in 2017 and really in many ways due to the influence of Will Zhuang here in York that we were able to develop more formal links with both Shanghai but in particular with Nanjing, and that led to the signing of a sister city agreement with the city of Nanjing that then triggered invitations to go and take part in historical and cultural exhibitions in Nanjing itself.
So that first visit to Nanjing in June 2018 for me was a real eye-opener. There's one thing to read about and to look at photographs of Nanjing City walls. It's a completely different experience to go and stand on them and get a feel for the scale and the monumentality of those structures. I mean, York city walls are the best preserved medieval and earliest city walls in the United Kingdom. They are just over 3 kilometers long. Nanjing city walls are 35 kilometers long. They are nearly 30 meters high in places. They are absolutely immense structures.
People’s Daily Online: Building upon the establishment of the sister city agreement and an amicable first interaction, did you get to visit other places in China, and what were the things that caught your eye while touring these places?
John Oxley: I was really interested in exploring the narratives around outstanding universal values. So, after the visit to Nanjing had finished we then visited Suzhou and went back to Shanghai, where I met various people and I talked at the Department of Architectural Studies at Jiaotong University in Shanghai, and made some really good links with the academics there.
I then continued my visits, and I went to Xi’an and Dunhuang to look at those two locations. And you know, the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor and the Terracotta Army are both World Heritage sites but the old city of Xi’an within its walls is not.
So, for me, I came back from that visit and my mind was just completely sort of buzzing with the possibilities of learning from that Chinese experience of how they'd use World Heritage to promote concepts of place, how they'd use World Heritage to develop a particular type of cultural tourism, and how they were using the management frameworks to deal with World Heritage in those locations.
Discovering outstanding universal values

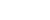
John Oxley (Photo/Lewis McCarthy)
People’s Daily Online: To acquire the status of World Heritage Site, both Nanjing and York must demonstrate outstanding universal values that appeal to all of humanity. In your opinion, what are the connections between the two cities’ pursuits?
John Oxley: We have developed and we have looked at the issue of outstanding universal value in relation to the historic core of York. And we've developed a narrative that is framed around the concept of York as an urban center for 2,000 years, which has its origins in the Roman military presence, but which then goes on to be a major administrative and ecclesiastical center and at center in the post-Roman period.
Going back to Nanjing, I see a lot of similarities between the narratives that Nanjing are trying to develop in their World Heritage bid and the narratives that we are trying to develop here in Europe for our World Heritage bid as well. I think there are universal values in how both cities came to be - from an early military flashpoint closure and then gradually taking up more spaces and incorporating different parts of the landscape in smaller pieces. We could both draw on each other's experience of constructing narratives about outstanding universal value and applying them to these two places.
People’s Daily Online: In addition to the universal values reflected in the history and development of both cities, what contemporary elements do you consider equally important to the World Heritage Site application?
John Oxley: The local context is incredibly important. And I'm sure from the conversations I've had with, for instance, the voluntary guides on the walls and at the City Walls Museum in Nanjing, that the pride and the sense of identity that the walls and the heritage of the city of Nanjing give to them is actually very similar, if not identical to what you get when you talk to the voluntary guides who work in the York Minster or the people who work with the Friends of York Walls.
And I think here in York, the heritage of the city clearly informs the sense of identity that the people who live here have about being in York, being someone who is from the city of York. So that heritage, although it speaks to a universal audience, is perhaps in many ways more important for how the local population, how the people who live in there interact with and deal with the heritage of the city. It's that sense of identity. And I think what we're trying to do in terms of developing that World Heritage narrative of outstanding universal value in York is trying to marry the unicycle vocabulary about outstanding universal value with those concepts of local identity.
People’s Daily Online: You have shared with us the core universal values of the city walls of York and Nanjing. Looking forward, what is the next step for York’s pursuit of World Heritage status, and, now that you have retired from the position of City Archaeologist, for you personally?
John Oxley: York's World Heritage journey started in 2006 when the then Lord Mayor, Janice Hopton, asked the question, should York be a World Heritage site? And so, I was involved at the very beginning. From 2006, we established a steering group, and I've taken a leading role in that steering group. We applied in 2010 to be placed on the tentative list of the UK nomination of World Heritage but were unsuccessful. But we were also advised by the expert panel that had given advice to the governments that we should apply next time. So, we had continued our work and in 2022 our bid was successful.
The United Kingdom only nominates one site every year and we are looking to have as much work done as we can to support a nomination to the World Heritage Committee in 2027. So, I see my role over the next four years as working very closely with United Kingdom World Heritage experts, but also working as closely as possible with World Heritage experts in places like China, where we already have good contacts and good networks in Shanghai, in Suzhou, in Nanjing and in Xi'an.
And again, look at what we can learn from their experience, from the experience of World Heritage cities in China, both in constructing a bid and in managing a place so that we can manage the outstanding universal value of these places.
Photos
Related Stories
- UNESCO World Heritage status invigorates conservation of China's old tea forests
- Hangzhou farmers begin harvesting Longjing tea leaves
- Beijing releases plan for Central Axis protection ahead of world heritage list application
- Irrigation project in Jiangsu gets world heritage designation
- Three more Chinese irrigation projects designated world heritage structures
- World Heritage Sites in China: Chengde Mountain Resort
Copyright © 2023 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.