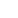Guardians dedicate decade to protecting endangered crested terns
HANGZHOU, Aug. 13 (Xinhua) -- The Chinese crested tern, known as the "bird of legend," is among the critically endangered tern species around the world. During this year's breeding season, a total of 45 chicks hatched on small islands in east China's Zhejiang Province.
The miracle of the births of these little creatures stems from efforts of ornithologists, relevant governing bodies, and social volunteers from all over the country. Since 2013, they have collaborated unwaveringly to help the species establish families and breed on small islands in the province.
Thanks to these efforts, the number of adult Chinese crested terns spotted in eastern Zhejiang has grown from less than 20 to nearly 150 over the past decade.
The Chinese crested tern was first recorded in Indonesia in 1861, but seemed to vanish after the 1940s. Ornithologists once believed that this species was possibly extinct.
However, more than 60 years later, this seabird was rediscovered on offshore islands along the coastal areas of eastern Chinese provinces of Fujian and Zhejiang.
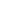
Since 2013, researchers and volunteers have implemented artificial attraction and population resumption techniques on several islands in Zhejiang. Simulated birds, audio recordings of tern calls and a variety of other methods have been used to attract Chinese crested terns back to boost nesting and breeding.
Ding Peng works for a national nature reserve in Zhejiang's Xiangshan County. He was also one of the first volunteers to take part in the Chinese crested tern restoration project.
Between April and August, Chinese crested terns usually follow their close relatives, the greater crested terns, to the islands in eastern Zhejiang for breeding.
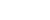
"The most important responsibility of the volunteers is to observe, record and protect their breeding process. At the same time, they need to eliminate threats to the terns from the likes of snakes, rats and birds of prey," the 33-year-old said.
In 2017, this project began recruiting island-based seabird monitoring volunteers from the general public, and it receives hundreds of applications every year from people from all walks of life, including doctors, scholars, retired civil servants, university graduates, business owners, and freelancers.
So far, nearly 30 volunteers have taken part in the project on the islands.
Life on these remote islands is very challenging. Volunteers have to rely solely on solar power, while nature reserve staff transport and provide the fresh water and food needed by the volunteers. The moist and sultry weather and the presence of plenty of mosquitoes are additional challenges. Despite these hardships, volunteers remain enthusiastic about protecting these rare seabirds.
He Jibai, 27, a volunteer from Chengdu, used to be a wildlife protector, and this past experience gave him more confidence in challenging the tough environment on the islands. He arrived there in late April and his monitoring work is scheduled to last until early September.
Before dawn, He and his colleagues need to check the monitoring equipment to make sure that the birds are safe at the breeding site at night. After that, they take shifts in conducting ongoing observations from a nearby hut. They must later compile and archive the whole day's data, and share their stories about life on the islands on the project's official social media account.
"I hope that our actions will inspire more people to protect wildlife around them. That is the value of our work," He said, adding that his fellow volunteers also share the hope that future generations will be able to witness the beauty of these seabirds.
(Intern Guo Qianchen contributed to the story.)
Photos
Related Stories
- Egret habitat enjoys preservation in key petroleum refinery plant
- White-headed langurs spotted in S China's Guangxi
- South China tiger population rises amid conservation efforts
- Yangtze finless porpoises under well protection with improved ecological environment
- Wildlife in Altun Mountains in NW China's Xinjiang
Copyright © 2023 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.