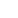Chinese scientists discover mating-swarms in early mayfly fossils
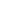
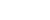
NANJING, June 8 (Xinhua) -- Chinese scientists said on Wednesday that they have discovered a new layer of mayfly fossils dating back 180 million years that shows the precious scene of mating-swarm behavior, the earliest known evidence of such behavior in insects.
Researchers from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS), and the Guangxi Institute of Geological Survey found the new layer, which contains 381 individual mayflies, in the city of Hezhou, south China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.
"Mating-swarm behavior was previously known only in crown mayflies. However, our finding reveals that such complex behaviors were already well established in stem-group mayflies by the Early Jurassic," said Wang Bo, a researcher with the NIGPAS.
"This finding represents the earliest evidence of mating-swarm behavior in insects," said Wang.
According to the expert, extant mayflies spend most of their lives in the aquatic environment as nymphs, and the adults commonly live from as little as 1-2 hours to a few days. During their short adult phase, the males form dense aggregations, and the females must find mating partners while flying in and through large swarms, wherein they copulate and ultimately locate a suitable place to deposit eggs.
The results of the research have been published in the journals Geology and Historical Biology.
Photos
Related Stories
- Chinese scientists find new gene to improve wheat yield
- Chinese scientists reveal molecular mechanism behind rape yield improvement
- Chinese scientists take inspiration from cobwebs to tackle freshwater scarcity
- Chinese scientists find fossil of new marine reptile with "incredibly long" tail
- Chinese scientists develop trajectory planning system for collision-free flight of drone swarms
Copyright © 2022 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.