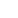Why is the EU wary of cutting off Russian energy?
* Over 40 percent of the EU's natural gas and 25 percent of its oil consumption come from Russia, and there has been a consensus among European countries that the EU's dependence on Russian fossil fuels should be reduced.
* The EU unveiled a plan to reduce energy imports from Russia, which is striving for independence from Russian fossil fuels well before 2030.
* As the bloc is far from reaching energy self-sufficiency, it appears to be a daunting and almost unattainable goal to reduce its reliance on Russia.
BRUSSELS, March 23 (Xinhua) -- The European Union is under mounting pressure from Washington to ban Russian energy imports as European leaders and U.S. President Joe Biden are set to meet and discuss deterrence measures against Russia at a summit here on Thursday.
However, member states of the bloc have not reached an agreement yet on whether a ban would be slapped on Russian energy in the EU.
"Europe's supply of energy for heating, mobility, electricity and industry currently cannot be secured in any other way," German Chancellor Olaf Scholz said at an EU leaders' summit in France earlier this month.
UNBEARABLE BAN
Over 40 percent of the EU's natural gas and 25 percent of its oil consumption come from Russia.
Germany has been holding on to its rejection of an abrupt ban. The country's Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock argued that the proposed oil embargo was a "question of how much we depend on oil" from Russia.
Other German leaders echoed Baerbock's concern. Minister for Economic Affairs and Climate Action Robert Habeck warned on Saturday that his country would not have enough gas to heat homes and keep industry going next winter if it does not obtain more gas and if deliveries from Russia are cut off.

Photo taken on March 18, 2022 shows diesel and gasoline prices displayed on a board at a gas station in Frankfurt, Germany. (Photo by Armando Babani/Xinhua)
Other EU members, such as Austria and Finland, have also warned against hastily banning energy imports from Russia.
The sanctions imposed by the United States and Britain on Russia's energy sector in response to Russia's military operation in Ukraine have already sent shockwaves across the world's energy markets.
"The implications of a potential loss of Russian oil exports to global markets cannot be understated," the International Energy Agency said in a report released last week.
According to the agency, Russia's oil production disruptions could lead to the biggest supply crisis in decades.
The prospect of an EU ban on Russian oil imports has already stirred the global energy market. On Monday, the crude price jumped more than 7 percent to 115 U.S. dollars a barrel as European diplomats were debating a possible ban on Russian energy imports.
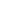
Surging oil prices have pushed transport companies to the brink of bankruptcy in Spain, where truck drivers started a national strike a week ago.
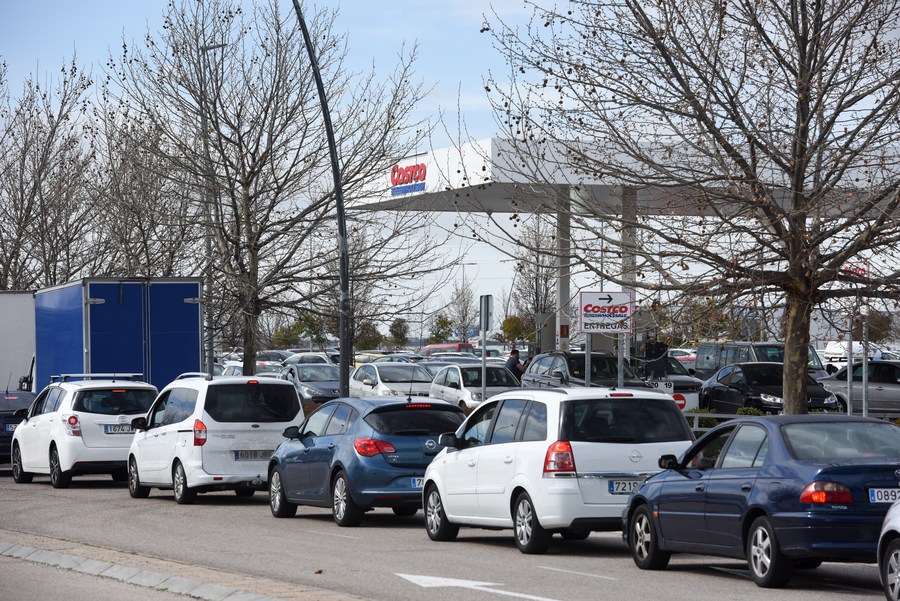

Cars wait to be refueled at a gas station amid rise of fuel prices in Madrid, Spain, March 12, 2022. (Photo by Gustavo Valiente/Xinhua)
As the strike enters its second week, the disruptions to transport are causing food shortages, and certain areas in northern Spain are even at the risk of running out of tap water.
The knock-on effect of energy price spikes has sent the prices of many other items skyrocketing in Germany. The German Farmers' Association said that the price of fertilizer is five times that of the same period last year.
Association President Joachim Rukwied said he was convinced that food prices would climb because farmers and food processors would have to pass the inflated costs on to customers.
The European Central Bank has already lowered its projection for economic growth in the eurozone to 3.7 percent this year.
UNATTAINABLE INDEPENDENCE
There has been a consensus among European countries that the EU's dependence on Russian fossil fuels should be reduced, if not ended altogether.
The EU unveiled a plan on March 8 to reduce energy imports from Russia. According to the plan called REPowerEU, the EU is striving for independence from Russian fossil fuels well before 2030.
By diversifying gas supplies, speeding up the rollout of renewable energy, and replacing gas in heating and power generation, the EU is attempting to reduce its demand for Russian gas by two-thirds before 2030.
In a post on social media, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen proposed that the EU should phase out Russian fossil fuels by 2027.
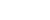
Considering that the bloc is far from reaching energy self-sufficiency, it appears to be a daunting and almost unattainable goal to reduce its reliance on Russia, which supplies around 10 percent of the world's oil demand.

Closed pumps are seen in a petrol station in Manchester, Britain, March 17, 2022. (Photo by Jon Super/Xinhua)
Even if the two members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries -- Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates -- with the largest spare capacity on standby are willing to beef up production, the shortfall in supplies in the event of the loss of Russia cannot be filled, according to analysts.
European officials have recently tried to convince some Gulf countries, including Saudi Arabia and the UAE, to increase their production to tame the soaring price of oil.
Saudi Arabia and the UAE have enjoyed a windfall from the oil price spikes since the Russia-Ukraine conflict erupted and categorically rejected calls to raise oil production. Instead, they made it clear that they would stick to the "OPEC Plus" commitment, under which OPEC members and Russia would increase oil production at a controlled pace.
Photos
Related Stories
- Russia urges Washington to quit escalating tensions
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict warrants a new European security mechanism
- US is reestablishing a new Inquisition using Russia-Ukraine crisis as excuse
- Unholy Crusade: White House leads KOL on anti-Russia propaganda, Western ‘rights groups’ turn blind eye to hate speech
- EU scrambles to shake off dependence on Russian energy amid Ukraine conflict
Copyright © 2022 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.