Why China's climate change dedication credible and attainable
China and the United States on Wednesday released the China-US Joint Glasgow Declaration on Enhancing Climate Action in the 2020s at the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP26) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
Both sides will "recall their firm commitment to work together" to achieve the 1.5℃ temperature goal set out in the 2015 Paris Agreement, the declaration said.
"China will scale up its Intended Nationally Determined Contributions by adopting more vigorous policies and measures. We aim to have carbon dioxide emissions peak before 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality before 2060," Chinese President Xi Jinping said at the general debate of the 75th session of the United Nations General Assembly via video on Sept 22, 2020.
In the face of global warming, China pledged to realize carbon neutrality in a shorter timespan than developed countries.
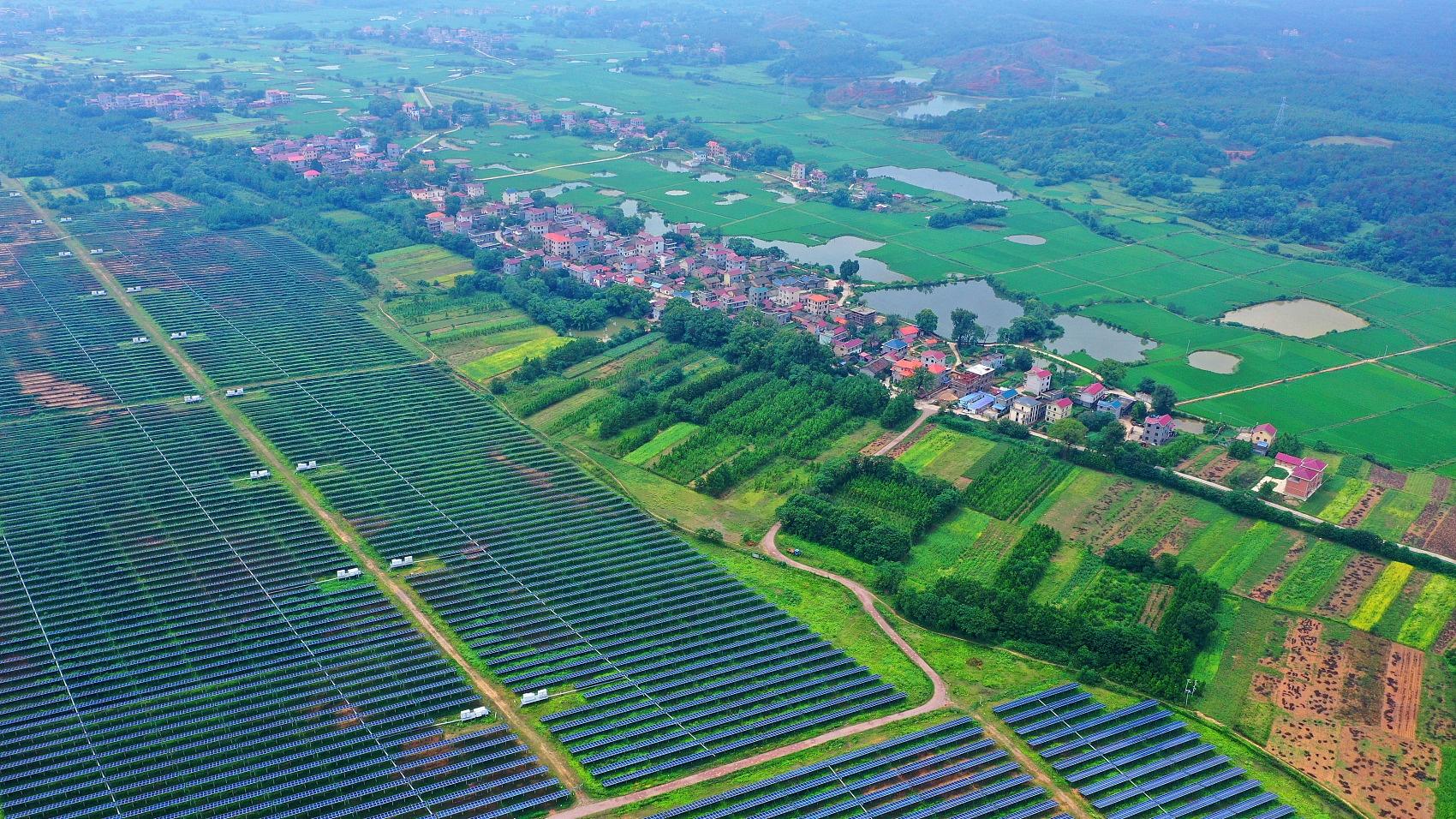
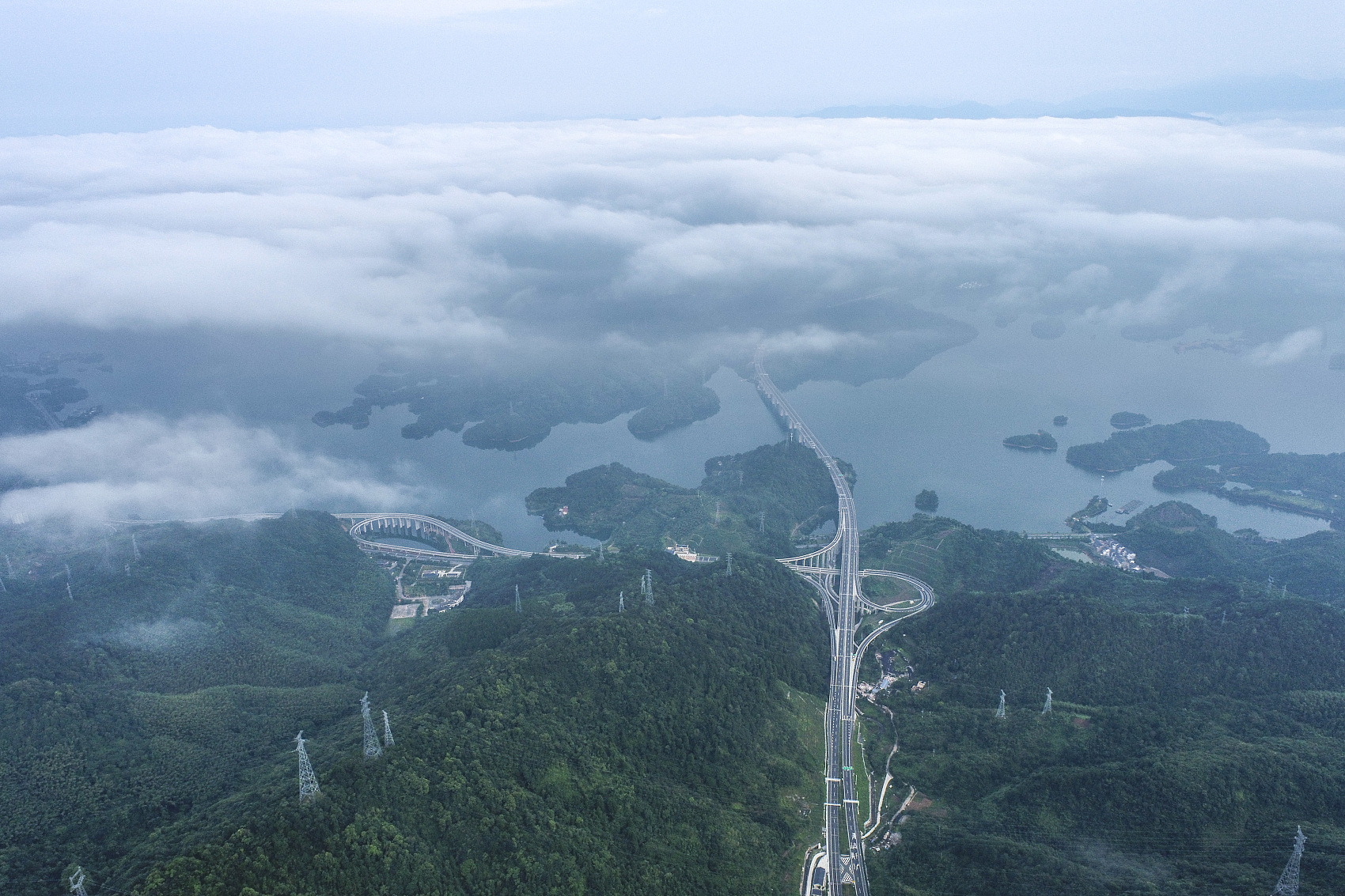


China is undergoing the world's steepest decline in carbon emission intensity and is expected to take the shortest time in history to transit from carbon peak to ultimate carbon neutrality.
So what exactly has China done?
What challenges did Beijing encounter?
What progress has been made?
Here are the answers.
(Produced by Zhao Dantong, Bai Yuanqi and Lin Rui; interns Luo Tianya, Lv Kaiying and Xu Shilin also contributed to the story)
Photos
Related Stories
- China contributes to global carbon emissions reduction
- All lip service, no actions -- Developed countries urged to walk the talk on climate crisis
- A divided America casts a shadow on global response to climate change
- China urges developed countries to intensify efforts on climate change
- U.S. withdrawal from Paris Agreement wastes world 5 years to tackle climate change: Chinese envoy
Copyright © 2021 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.