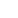Maturing apple planting industry brings bountiful returns to farming community in northwest China’s Gansu
“Five years ago, when the local government suggested that we grow apple trees as a channel to increase our incomes, no one said yes,” recalled Gyatsoman, a woman in her twenties. Today, apple planting has become a pillar industry in his hometown.
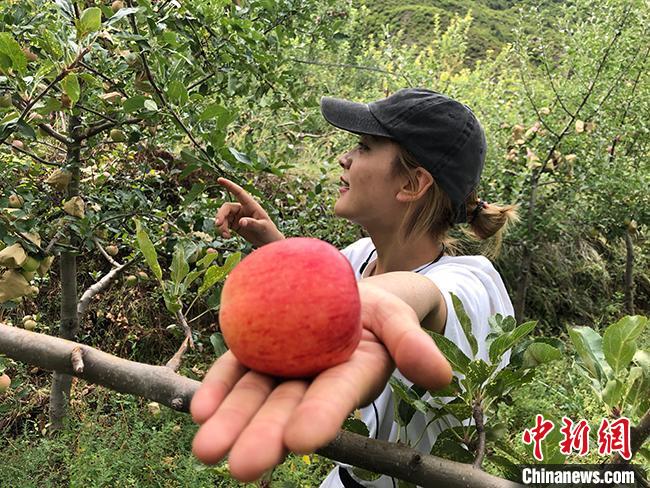

Gyatsoman shows an apple in her orchard. (Photo/Wang Muyu)
In the past, villagers in Cirina village in Wangzang township, Diebu county, Gannan Tibetan autonomous prefecture in northwest China’s Gansu province made a living by growing crops such as wheat, high-land barley, and buckwheat, which generated low yields and with the earnings having been just barely enough for their continued subsistence. After an anti-poverty campaign kicked off in the locality, the local government came to realize that it was time that they changed their approach to farming in a renewed attempt to lift everyone out of poverty.
It was at this point when the villagers decided to begin growing apple trees in the surrounding river valleys, which provided comparatively favorable land and climate resources for planting trees. They also acquired farming knowhow and experience from other places that already had mature apple planting industries. However, at first, the idea of planting apple trees was not widely embraced by the villagers, especially the senior residents in the community, who had thought that planting apple trees was a risky business due to a lack of supporting technologies. They also feared that the apples might not sell well.
Taking these doubts into consideration, the village made a decision that cadres and Party members should be the first ones to try out growing apple trees, with all the other villagers having the choice to enter the business based on the performance of the initial apple orchards. When the villagers saw that the apple trees produced high-yield and high-quality fruits, and with the returns generated from the apples having been higher than those from other crops, they went ahead with plans to plant their own apple trees, as did the residents in neighboring villages.

A signboard with a buyer’s information on it in an apple orchard. (Photo/Wang Muyu)
To boost agricultural production, the village moved to transfer the land-use rights of 130 farmers, utilizing about 1,200 mu (80 hectares) of land in all for apple planting. It also built a storage facility and a sales center that could provide services for more than 500 farmers.
The township rolled out a creative marketing strategy to boost apple sales. Based on the adopted approach, a customer could purchase apples from any grower and he or she had the option to purchase all of the apples produced by any given tree. The customer could also receive timely updated information about the selected apple trees from the grower, as well as receiving a guarantee that no chemical fertilizers or pesticides would be used in the growing of the trees, with all the apples produced exclusively for the buyer as opposed to being sold onward to secondary customers.
Gyatsoman sold three of his apple trees to a customer from the city of Huizhou located in south China’s Guangdong province. During the seven-day National Day holiday, the buyer took his family to Gyatsoman’s apple orchard to see their trees. They also picked the apples and brought them back home as gifts for friends and relatives.
Photos
Related Stories
- Farmers increase income selling apples on a train in SW China
- County in northwest China's Shaanxi boosts development of apple industry
- Apple announces plans to establish research and development center in Shenzhen
- Have you ever tasted 'darkness food'--apple with sliced chicken
- "Luxury" art apples debut in Shanghai
- Apple Maps help inbound travellers plan routes
Copyright © 2021 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.