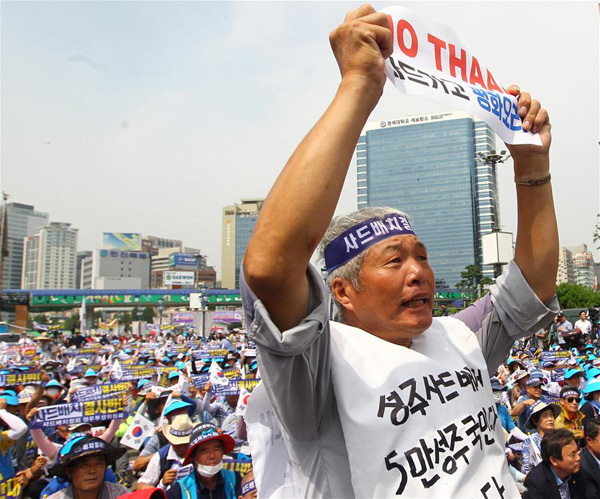



A man from Seongju county holds a banner to protest against the deployment of the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD), during a rally in Seoul, capital of South Korea, on July 21, 2016. More than 2,000 people from Seongju county, where one THAAD battery will be deployed, gathered at a square in Seoul for a rally on Thursday, to protest against the deployment of THAAD. (Xinhua/Yao Qilin)
Despite the strong opposition of China, the United States and the Republic of Korea have agreed to deploy the Terminal High-Altitude Area Defense system in the ROK. Although the US claims THAAD is aimed at countering the "nuclear threat" posed by the Democratic People's Republic of Korea", it is actually targeted at China.
Why is THAAD's deployment in the ROK strongly opposed by China?
THAAD will undermine the regional strategic balance in East Asia and create more obstacles to the peaceful settlement of the Korean Peninsula nuclear issue. When the strategic balance of a region is broken, an arms race follows and regional disputes and conflicts intensify.
The Korean Peninsula is one of the few places in the world where the fear of war is still real. The peninsula nuclear issue has been threatening security in the region for over a decade, and negotiations, including "the Six-Party Talks", to settle the issue have been stalled. In such a sensitive region, THAAD's deployment could open the door to a military confrontation.
One way of rectifying the strategic imbalance is for the US and the ROK to rescind their agreement to deploy THAAD. The second way is for Beijing to strengthen its nuclear capability, for once THAAD is deployed in the ROK, major parts of China will be under its anti-missile system umbrella.
The deployment of THAAD in the ROK is part and parcel of the US missile defense system in East Asia, a region of strategic importance to the US where it sees China challenging its "DLP" (dominance, leadership and primacy). The US has singled out China as the target for its "rebalancing to Asia" strategy. And THAAD is an indispensable component of that "rebalance".
John J. Mearsheimer of the University of Chicago and Stephen M. Walt of Harvard University recently published an article in Foreign Affairs outlining "rebalancing to Asia" strategy as a superior "grand strategy" to be applied seriously by the US in East Asia and Europe. These two neoconservative theorists have identified China as "likely to seek hegemony in Asia" and call on the US to undertake major efforts "to prevent it from succeeding". "Rebalancing to Asia" first calls for the US to "rely on local powers to contain China". Should that fail, the US may "have to throw its considerable weight behind them".
THAAD is a case in point. The US' involvement in the South China Sea issue-supporting the Philippines in its political farce of seeking "international arbitration" and the exhibition of force by the US Navy and Air Force-is another example of its "rebalancing to Asia" strategy.
The US is used to thinking and acting as a hegemonic power. But we live in an era of globalization where countries are more interdependent than ever. No country can be "balanced" or "rebalanced" away as the US wishes. As such, the deployment of missile defense systems in Eastern Europe and East Asia will hurt global stability.
THAAD's deployment will worsen the divide in East Asia, where regional arrangements for economic growth are shaped with China at its core while regional security is assumed to be based on the US-centered military alliances. Should this contradictory situation develop further, neither regional economic growth nor security can be sustained.
In short, THAAD is detrimental to the regional security of East Asia. No country can expect to achieve absolute security at the expense of other countries' insecurity. East Asia should enjoy peace and stability based on common and cooperative security. Therefore, the countries involved in the power game should reconsider their ill-conceived decisions in order to restore the regional strategic balance.
The author is former vice-minister of the Overseas Chinese Affairs Office of the State Council and former vice-minister at the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 Who Will Fit The Chinese Roles In Game Of Thrones?
Who Will Fit The Chinese Roles In Game Of Thrones? China's Hubei Shennongjia added to World Heritage List
China's Hubei Shennongjia added to World Heritage List "Straddling bus" starts production in east China
"Straddling bus" starts production in east China Girl goes viral for finger-long toes
Girl goes viral for finger-long toes Five made-in-China hi-tech breakthroughs
Five made-in-China hi-tech breakthroughs HK-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge to open to traffic
HK-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge to open to traffic China opens its first combined transport service to Nepal
China opens its first combined transport service to Nepal Students take stylish bikini graduations photos
Students take stylish bikini graduations photos Charming dancing students pose for graduation photos
Charming dancing students pose for graduation photos Top 10 livable Chinese cities
Top 10 livable Chinese cities Top 20 hottest women in the world in 2014
Top 20 hottest women in the world in 2014 Top 10 hardest languages to learn
Top 10 hardest languages to learn China’s Top 10 Unique Bridges, Highways and Roads
China’s Top 10 Unique Bridges, Highways and Roads Nation commemorates 40th anniversary of Tangshan earthquake
Nation commemorates 40th anniversary of Tangshan earthquake Viewers give Guo Jingming's ‘Ice Fantasy’ the cold shoulder
Viewers give Guo Jingming's ‘Ice Fantasy’ the cold shoulder Tiger tragedy highlights zookeepers’ failings in poorly-regulated industry
Tiger tragedy highlights zookeepers’ failings in poorly-regulated industry Legalization of tiger product trade slammed by environmentalists
Legalization of tiger product trade slammed by environmentalistsDay|Week