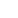China's Xiamen combats emerging pollutants
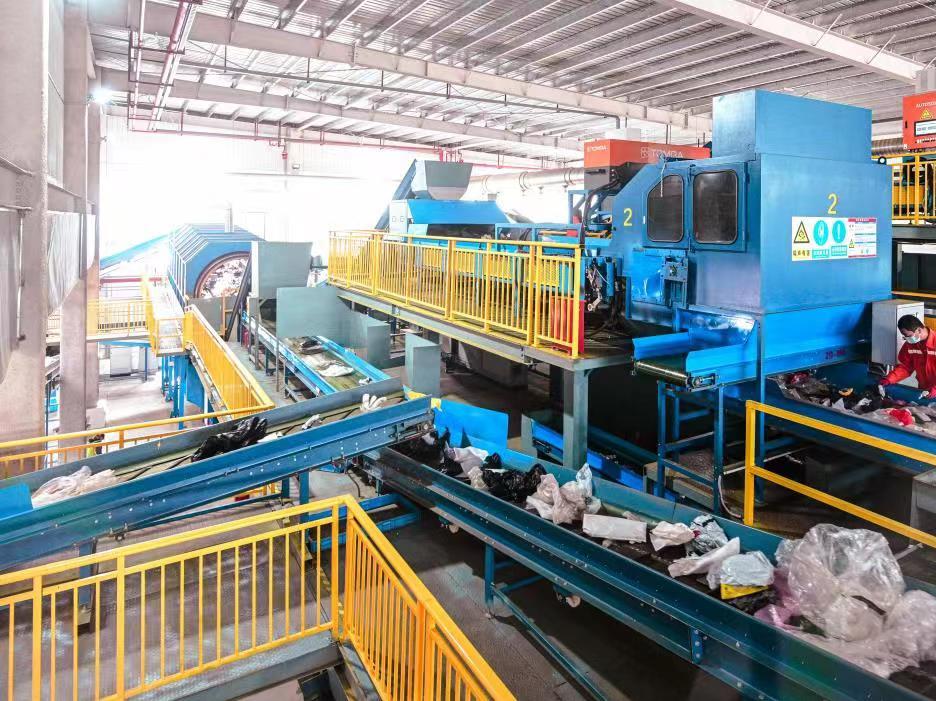

Photo shows the Xiamen low-value recyclables sorting center in Xiamen, southeast China's Fujian province. (Photo from Xiamen Daily)
At 8 a.m., Huang Chunyi, a resident of Lianqian neighborhood in Siming district, Xiamen, southeast China's Fujian province, headed out for work, taking along three bags of household waste to a collection point in her residential complex.
"One bag is kitchen waste, one is general waste, and the third holds recyclables like cardboard, plastic bottles, and plastic packaging from a courier box," she said.
"Plastic that is properly recycled can become a reusable resource, but plastic discarded at will may eventually turn into emerging pollutants such as microplastics," Huang noted. Having learned a great deal from public education campaigns on waste sorting, she has become particularly attentive to environmental protection.
In Xiamen, all recyclable waste collected from homes is transported daily to a specialized sorting center for low-value recyclables. Inside the facility, an intelligent sorting system operates alongside high-speed conveyor belts. This system identifies difficult-to-process materials and directs them into specific storage bins.
There, a wide range of paper and plastic products is sorted into 16 refined categories before being recycled into regenerated materials.
"Plastics account for over 60% of the low-value recyclables we process. Without timely collection and treatment, they can pollute the environment and eventually degrade into emerging contaminants such as microplastics measuring less than five millimeters," said Xie Yibin, operations director at the sorting center.
Emerging pollutants, now widely discussed both in China and abroad, mainly include persistent organic pollutants regulated by international conventions, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, antibiotics, and microplastics.

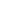
A staff member of a laboratory of the Xiamen municipal environmental monitoring station conducts an experiment on emerging pollutants. (Photo provided by Xiamen municipal environmental monitoring station)
According to Luo Zhuanxi, professor of environmental science and engineering at Huaqiao University in Fujian province, emerging pollutants refer to toxic and hazardous chemical substances characterized by biological toxicity, environmental persistence, and bioaccumulation, posing significant risks to ecosystems and human health.
"I never realized emerging pollutants were so close to our daily lives," said Zhang Ruixing, engineering director of an electronics design and manufacturing company.
Following the release of a 2023 edition of a list of key controlled emerging pollutants, the company, under the guidance of environmental authorities, immediately reviewed all its raw materials.
"After electronic components are soldered onto circuit boards, cleaning solvents are used to remove organic residues from the solder. The solvent we previously used contained dichloromethane, an emerging pollutant listed in the catalog and a volatile organic compound. For environmental safety, we decided to replace the material as soon as possible," Zhang explained.

Tourists visit Xiamen's iconic scenic area, Gulangyu Island. (Photo/Hu Xuejun)
In fact, traces of emerging pollutants can be found in many aspects of everyday life. "Paints and leather products may contain persistent organic pollutants; some personal care products and industrial waste may contain endocrine disruptors; and antibiotics are widely used in the medical sector," Luo explained.
In recent years, Xiamen has strengthened coordinated governance of emerging pollutants and explored environmental risk control covering their entire life cycle.
"Pollution prevention at source represents an eco-friendly strategy for addressing emerging pollutants, though its implementation remains challenging," explained Feng Weiguo, an official with the soil environment and solid waste management division of the Xiamen municipal bureau of ecology and environment.
Leakage of such pollutants can occur throughout their entire lifecycle, from production and use to final disposal, which heightens the demands on both monitoring and regulatory oversight. Therefore, effective management calls for coordinated efforts to enhance whole-life-cycle control, spanning from industrial processes to end-of-pipe treatment.
"Our company produces about 5 million units of various products each month, so any change in processes or materials must undergo rigorous verification," Zhang said. The company conducted third-party component testing and laboratory performance verification, then compared factors such as composition, cost, and cleaning effectiveness before selecting suitable materials for small-batch trial production. "It took six months, and we are now using a wholly new material."
"Focusing on key industries, we have introduced sector-specific technical standards and established chemical substance inventory systems to encourage enterprises to upgrade their technologies, enhance their environmental image and brand value, and improve market competitiveness," Feng noted.
In addition, Xiamen has issued relevant regulations and technical guidelines requiring early scientific assessment at the project-approval stage, clarifying risk-prevention and control measures for toxic and hazardous chemicals and guiding enterprises to improve full-process environmental risk management mechanisms.
What can individuals do in daily life to help manage emerging pollutants?
"Consumers can reduce their exposure to emerging pollutants -- for example, by cutting down on plastic products, prioritizing biodegradable alternatives, and properly sorting waste to improve recycling," Luo said. He also advised consumers to check ingredient labels, opt for environmentally friendly goods, and use and dispose of antibiotics responsibly.
Photos
Related Stories
- Waste oil recycled into products in SW China's Sichuan
- New technology keeps waste facilities odor under control
- EU proposes new rules to reduce wasteful packaging
- China to improve utilization of industrial solid waste
- China endeavors to turn construction waste into resources
- China's first radioactive waste glassification facility operational
- China eats its fill as take-out boxes scaled back
- In green milestone, China to end solid waste imports
- China to ban all imports of solid waste from 2021
- Chinese customs seize over 2,000 tonnes of smuggled waste
Copyright © 2026 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.