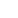Huishan in E China accelerates its shift toward new growth drivers

Photo shows the first-phase project of LandSpace's manufacturing base for reusable rockets in Huishan High-Tech Zone in Wuxi, east China's Jiangsu province.
Recently, Elon Musk, founder of U.S.-based SpaceX, commented several times on social media about Zhuque-3, a reusable rocket independently developed by Chinese aerospace company LandSpace, drawing global attention from the space sector.
At the same time, construction of LandSpace's future main manufacturing base for the Zhuque-3 rocket has entered its final phase in Huishan High-Tech Zone in Wuxi, east China's Jiangsu province.
Why did LandSpace choose Huishan High-Tech Zone for its production base? According to a company executive, "After evaluating multiple cities, we found that within a 50-kilometer radius of the zone, all the necessary raw materials and component suppliers are readily available. In particular, local suppliers can provide 90 percent of critical engine production materials."
Huishan High-Tech Zone has grown out of Luoshe township in Huishan district, Wuxi, a traditional industrial township with a solid manufacturing foundation and a complete range of industries. In 2021, Luoshe was approved to establish Huishan High-Tech Zone. That same year, it set its sights on emerging industries and launched the Wuxi Aerospace Industrial Park.
LandSpace is not the only company here that aspires to space exploration. JTSPACE, a private company in the burgeoning commercial space market, has built a production base in the zone for key components of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellites. By adopting integrated, standardized and modular design concepts, the company has made satellite manufacturing as efficient and streamlined as home-appliance production, helping commercial satellite production shift from small-batch, bespoke builds confined to laboratories to standardized, large-scale assembly-line manufacturing.
In orbit, commercial meteorological satellites operated by Tianjin Yunyao Aerospace Technology Co., Ltd. circle the Earth once every hour and a half, monitoring global weather patterns. Li Fenghui, chairman of the company, said the company placed its meteorological satellite R&D, manufacturing and data-application projects in Huishan because of the district's efficient administrative services and high-standard facilities. "In less than a month, we recruited nearly 20 professionals in meteorology," he noted.
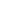
While the aerospace industry continues to push toward space and near-space frontiers, the low-altitude economy is steadily integrating into everyday work and life. At the Asia-Pacific headquarters showroom of Magnus Aircraft in Huishan High-Tech Zone, a Fusion 212 aircraft stands out. This two-seat light sport aircraft features a lightweight carbon-fiber airframe, with a top speed of 256 kilometers per hour. According to the company, more aircraft models, including the Fusion 212, are expected to be produced at the Huishan facility.

Photo shows a Fusion 212 aircraft exhibited at the Asia-Pacific headquarters showroom of Magnus Aircraft in Huishan High-Tech Zone.
Applications of the low-altitude economy are becoming increasingly diverse in Huishan. A drone-based blood delivery route now links Wuxi Central Blood Station with Wuxi Huishan District People's Hospital.
By integrating artificial intelligence and drone technologies, the route, with a blood cold-chain management system and a blood dispatch platform, addresses inefficiencies and traffic-related disruptions in ground transport.
As a result, emergency blood delivery time has been reduced from around an hour to just over 10 minutes, significantly enhancing medical support capacity and securing patients' precious "golden rescue time."

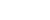
Engineers debug a humanoid robot at an embodied intelligent robotics industrial data center built by Miracle Automation in Wuxi, east China's Jiangsu province. (Photo/Zhu Jipeng)
Along this path toward renewal, traditional manufacturing in Huishan is accelerating its transition toward intelligent production. Miracle Automation, once a small mold-making factory, has grown into an internationally-recognized manufacturer of intelligent automation. In recent years, the company has made embodied intelligent robotics a key strategic focus, reaching cooperation intentions with several leading new-energy vehicle manufacturers on robotics applications.
Recently, an embodied intelligent robotics industrial data center built by Miracle Automation was put into operation. Covering about 7,000 square meters, the center integrates multiple functions, including real-world application training, simulated environment training, data collection, and multi-modal large-model training. In its initial phase, it can support the simultaneous training of more than 100 robots, providing a strong platform for the next stage of intelligent manufacturing development.
Photos
Related Stories
- Aerial rescue as community spirit soars
- Civil aviation show attracts eVTOL aircraft makers, with rising enthusiasm for winning type certificates
- Sky-high thrills amid Xinjiang's low-altitude tourism
- Liaoning in NE China seizes opportunities to develop low-altitude economy
- Low-altitude tourism activities become trendy among tourists in China's Hainan
- World's first tri-ducted wearable electric vertical takeoff and landing launched in Hangzhou
- Commercial flying cars gearing up for liftoff
- Futuristic food delivery lands at Fudan University
- From plowshares to propellers: how Chinese farmers are piloting agricultural modernization
- China to revise law, ensuring airspace allocation of low-altitude economic development
Copyright © 2026 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.