From open source to global solutions: China's expanding AI footprint
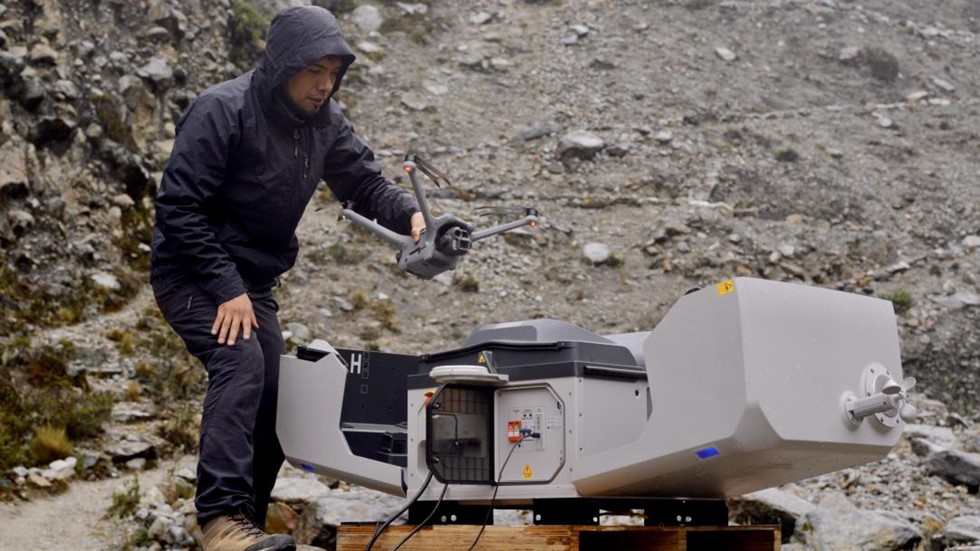

A Peruvian engineer conducts a glacier preservation mission in the Andes mountain range with a drone developed by Chinese company DJI. (Photo provided by DJI)
A recent report jointly released by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the open-source platform Hugging Face showed that Chinese-developed open-source large language models account for 17.1 percent of global downloads over the past year. This marks the first time China's share has surpassed that of the United States for the first time, reflecting a strategic advancement in the overall strength of China's AI industry.
According to the latest estimates by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, China's AI industry reached a scale exceeded 900 billion yuan ($128.87 billion) in 2024, representing a year-on-year increase of 24 percent. By September 2025, the number of AI enterprises in China had surpassed 5,300, accounting for 15 percent of the global total.
On this basis, the international impact of China's AI technology is evolving. It is transitioning from primarily leading through open-source contributions to driving global expansion practical applications. Meanwhile, its product offerings are shifting beyond standalone tool-based apps toward an integrated technological ecosystem that spans algorithms, platforms, and industry-specific solutions.
This transformation is closely linked to the in-depth implementation of China's "AI Plus" initiative. Driven by both supportive policies and market demand, Chinese AI enterprises have gradually developed the capability to deeply integrate technology with application scenarios through long-term practice.
Early efforts in product globalization efforts, initially focused on internet applications, are now accelerating their expansion into core areas of the real economy. These include urban governance, smart energy, transportation and logistics, and advanced manufacturing. This trend reflects a deepening convergence with worldwide demands for industrial digital transformation.

A teacher in a Thai school gives a Chinese class using an intelligent teaching system. (Photo/Shi Panpan)
In the Middle East, Chinese companies are integrating AI and Internet of Things technologies into national strategic projects such as Saudi Arabia's NEOM and the United Arab Emirates' Smart Dubai, helping build efficient resource management and urban security systems within challenging desert environments.
In Southeast Asia, industrial vision inspection and predictive maintenance solutions provided by Chinese AI enterprises have been deployed in electronics and auto parts factories in countries like Vietnam and Thailand.
The global expansion of Chinese AI companies has transcended mere product or service exports—they are now propelling the intelligent transformation of local industrial chains through technological empowerment.
The global reach of China's AI technologies represents not only a broadening of application scenarios but also an effective response to practical challenges in production and daily life.
In regions with dispersed populations or complex terrain, such as southern Europe and Latin America, Chinese industrial drones equipped with AI vision systems have become an important force in forest fire prevention and power line inspection. They have reduced traditional response times from hours to minutes, providing safety guarantee for remote communities.
Across Africa and South Asia, lightweight AI applications enable smallholder farmers to receive crop pests and diseases via mobile devices, providing immediate diagnostic and treatment guidance.
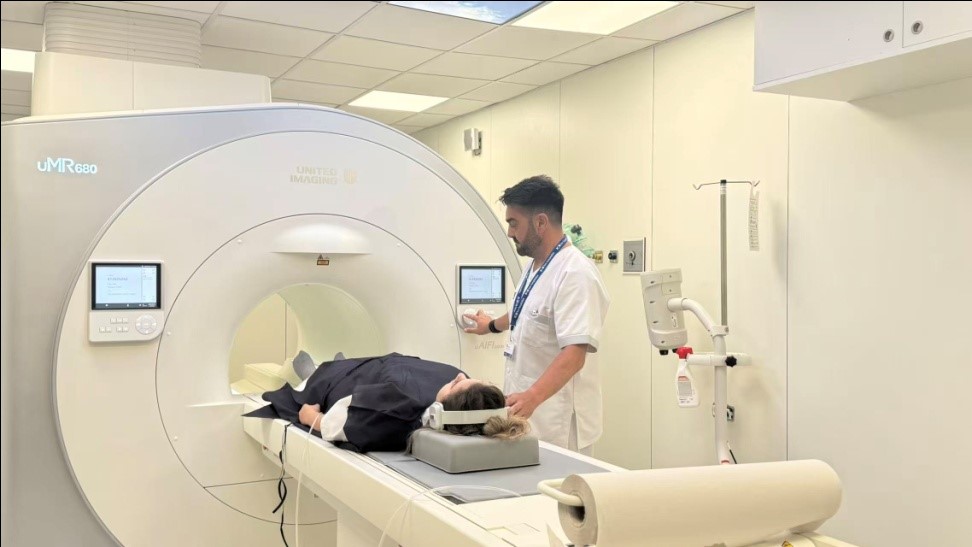
A doctor uses magnetic resonance imaging equipment developed by Chinese company United Imaging Healthcare at a hospital in Malaga, Spain. (People's Daily/Yan Huan)
These practices not only create commercial value but also elevate quality of life, enhance social resilience, and advance the global implementation of inclusive technological benefits.
China's competitive advantages in AI extends beyond technological innovation and application promotion to encompass active participation in global governance frameworks.
In response to governance challenges such as cross-border data flows, algorithm compliance and ethical security, China has consistently upheld principles including people-centered approach, AI for good, fairness, inclusiveness and collaborative governance, and has integrated these concepts into international governance practices.
The resolution on strengthening international cooperation in AI capacity building, proposed by China and adopted by the 78th session of the United Nations General Assembly, reflects recognition of China's approach by the international community and represents an important milestone in bridging the intelligence divide and promoting inclusive development.
Moving forward, Chinese AI enterprises will engage more deeply in global innovation networks through open collaboration and trustworthy practices. By contributing Chinese insights in areas such as rule-making, risk governance and capacity building, China will work with other countries to advance the building of a peaceful, secure, open, cooperative and orderly cyberspace.
Wei Kai is the director of the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute of the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology.
Photos
Related Stories
- Analyses predict deepened AI healthcare commercialization in China in 2026
- Synergy between mainland AI companies, HK market fosters new tech financing hub
- AI in China spots cancers doctors might have missed
- China's Jiangsu unveils AI action plan to boost smart economy
- Chinese AI startup tops global embodied intelligence benchmark
- MIIT targets 55% industrial internet platform penetration by 2028
Copyright © 2026 People's Daily Online. All Rights Reserved.